Big Tech's Push To Connect The Unconnected Signals Growth For Clean Tech

Now more than ever, access to connectivity is essential. As a result of the pandemic, all aspects of our lives were reinvented on virtual platforms, ultimately increasing our reliance on mobile connectivity and highlighting its importance across the globe. Now, a global effort is underway to connect the nearly 4 billion people around the globe who are not connected to the internet. Most importantly, global tech companies are investing in this effort, which provides investors opportunities to benefit from investing in technologies which power connectivity anywhere around the world. At the end of the day, connecting the entire globe will require innovative, clean infrastructure solutions.
The Market Opportunity For Clean Tech Around The Digital Divide
There are nearly 4 billion people around the world not connected to the internet. 93% of the world’s unconnected live in low and middle-income countries where implementing reliable ground infrastructure to power telecom sites is both challenging and cost prohibitive. The power system alone accounts for a significant proportion of telecom site costs, which means affordable off-grid power can be a critical component in enabling global connectivity. As a result, there is a major market opportunity for low-cost, reliable, off-grid power solutions to support connectivity.
In Sub-Saharan Africa especially, the telecom market has grown consistently over the past decade. In 2020, 30% of the population was using the internet, up from 6% in 2010, demonstrating the momentum behind the race to connect the world. A huge driver in this connectivity trend in Africa is the extremely young population. By 2050, the median age in Africa is expected to be 25, compared to a median age of 47 in Europe. Such a young population will be eager to gain access to the improved economic, and educational service opportunities which are available with a simple internet connection. Ultimately, the young population in Africa signals growth opportunity for the telecom market and the solutions which make it possible.
The Incentive of Big Tech To Connect The Unconnected
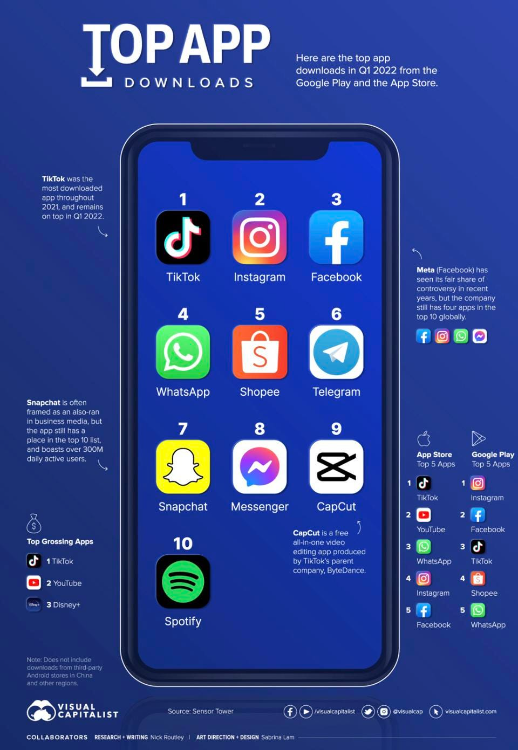
What many don’t often realize is that big tech platforms such as Meta (NASDAQ: META) have an enormous incentive to increase global connectivity. Meta owns four of the top 10 downloaded apps. When people gain connectivity, one of the first things they do is download a communication platform under the Meta umbrella to connect with family or friends. As a result, increasing connectivity will result in a major uptick in Meta’s user base, which gives them (and other large tech companies) an important stake in this game. As an example, between 2020 and 2021, Facebook’s daily active user base in the ‘Rest of the World’ and ‘Asia Pacific’ increased by 124 million. In Europe, the United States, and Canada, Facebook’s daily user base saw a slight decline in the same period. For tech supermajors like Meta, their growth opportunity lies in bringing the substantial unconnected population online in Africa and the Asia Pacific region, and their efforts are increasing the initiative’s momentum.
Corroborating this account, Meta has openly stated their mission to increase connectivity around the world, as Vice President Dan Rabinovitsj acknowledged, “One of the things that we realized is that actually getting people online to the internet, and also improving the speeds of the network once they’re online, is really critical. There’s a very clear business strategy and rationale for us to be investing this way.” Therefore, Rabinovitsj clearly emphasized the fact that global connectivity is a driver of company revenue, and therefore it is Meta’s mission, and other global tech firms as well, to bring everyone around the world online.
Big Tech’s Push For Global Connectivity
Big tech companies have been advancing the global initiative to connect the unconnected in a few ways. Meta has been investing in the development of the low-cost, innovative technologies and solutions required for worldwide connectivity. By funding the Telecom Infra Project (TIP), a collaborative group working to develop innovative solutions for global connectivity, Meta has helped develop the disruptive technologies needed to implement scalable connectivity. For instance, Meta’s Project SEISMIC targeted the use of smart technology to reduce costs and increase the reliability of off-grid power solutions for telecom sites. Project SEISMIC demonstrates how global tech companies are investing in clean tech solutions which make connectivity affordable and scalable anywhere in the world.
In addition to funding important organizations such as TIP, Meta has also directly invested in ground infrastructure to help bring more people online globally. For example, the tech giant has invested in 10,000 kilometers of terrestrial fiber cables around the world and 37,000 kilometers of sub-sea fiber cables to help improve internet speeds around the world. Investments such as these are crucial as they allow smaller companies to provide connectivity by sharing the infrastructure capital expenditure. Overall, what this demonstrates is that the global connectivity effort is not simply being championed by governments and non-profit organizations, but it has the full support of major tech players who are able to move the needle.
Ultimately, the global push to connect the world is being driven by major tech players. There is a significant market opportunity to bridge the digital divide and bring connectivity to inaccessible areas through low-cost off-grid solutions. Global tech companies are actively investing in the effort to increase global connectivity, which indicates strong growth for clean tech, and all players involved in the telecom market.